When a nearby star goes supernova, scientists will be ready
Earth's observatories hope to detect neutrinos and gravitational waves
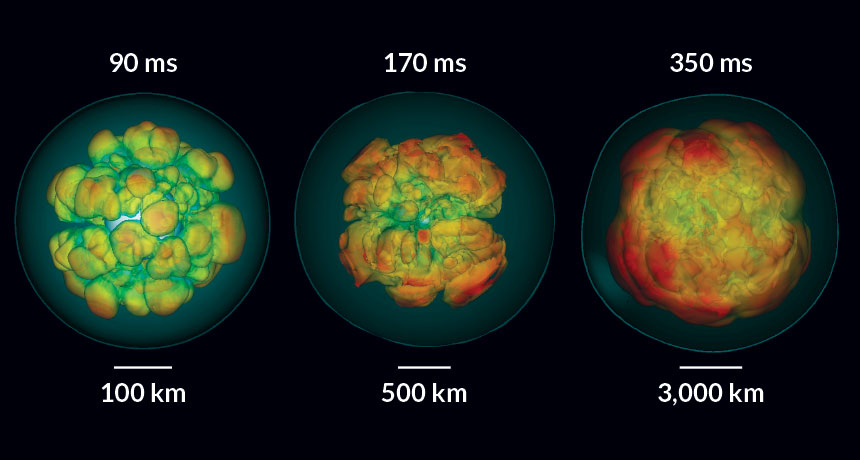
STELLAR SWOON A simulation of a supernova tracks the turmoil in the center of a dying star in the moments after its core collapses. The collapse creates a shock wave (blue line) that travels outward, blasting the star apart. Red colors represent material hurtling outward, blues represent inward motion. The surfaces of the lumpy shapes have equal entropy, which is related to temperature.
T. Melson, H.-T. Janka and A. Marek/Astrophys. J. Lett. 2015
Almost every night that the constellation Orion is visible, physicist Mark Vagins steps outside to peer at a reddish star at the right shoulder of the mythical figure.